If you don't have a Linux server. Please refer to How to purchase an instance.
Log in to the Linux server
When logging in to the cloud server, you need to use the administrator account and corresponding password. If you forgot the OS password, you can reset the OS password.
Administrator account: For Linux type instances, the administrator account is unified to root.
Connect the cloud server has two methods:
Method 1. In the action column of the cloud server list, click the [Connect] button to connect to the Linux cloud server through VNC:
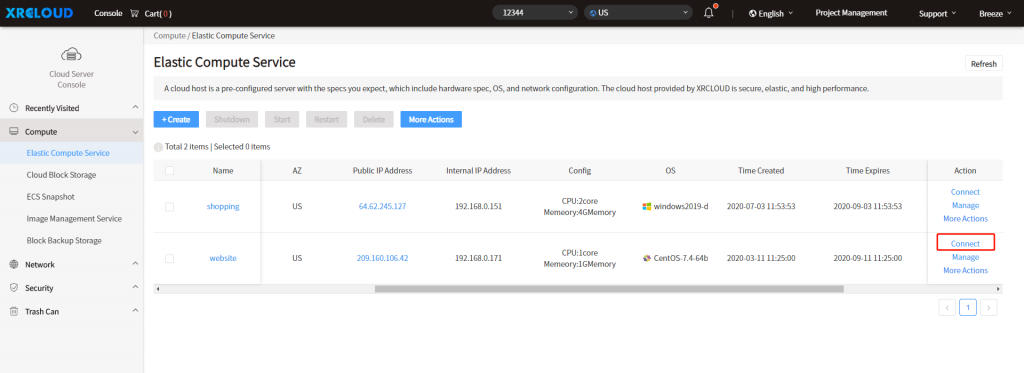
Enter the account name "root" and the OS password to log in.
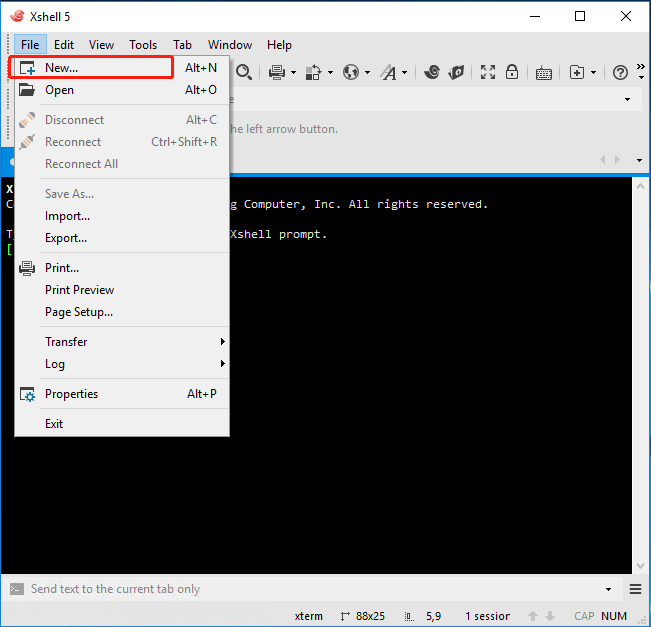
Method 2. Download the Xshell tool. After the installation is completed, running the Xshell.
Please enter your public IP Address.
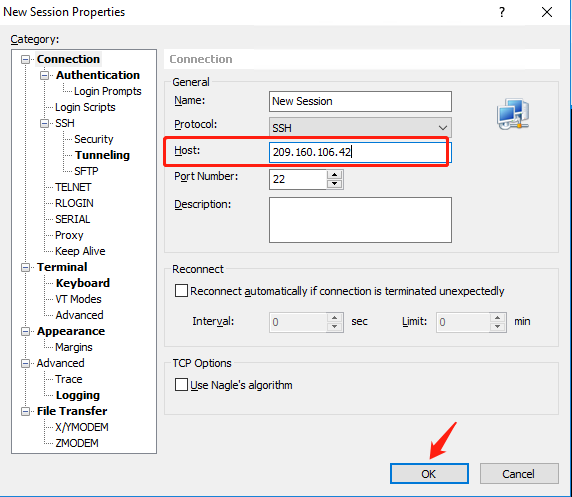
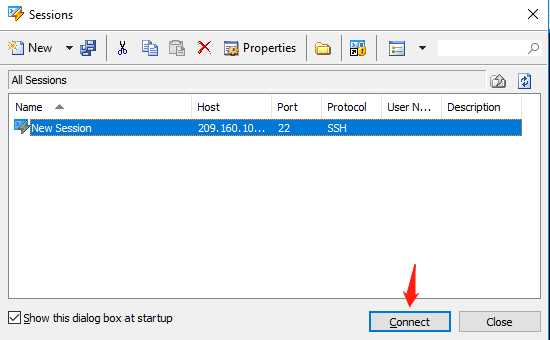
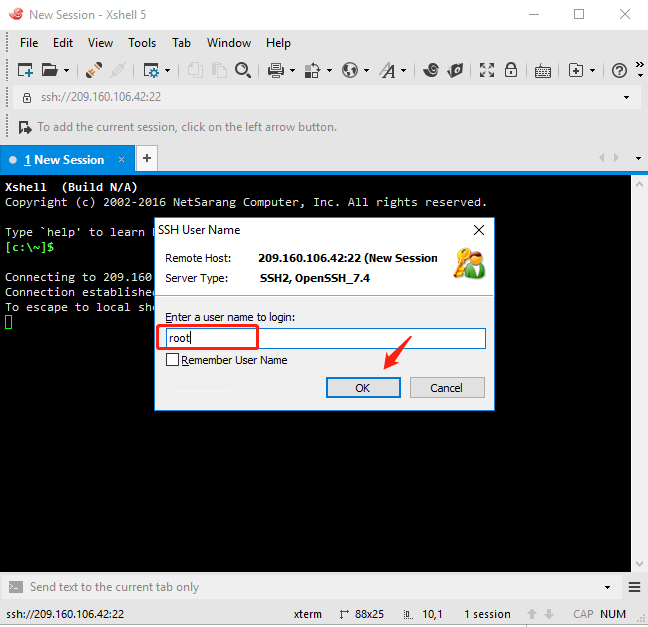
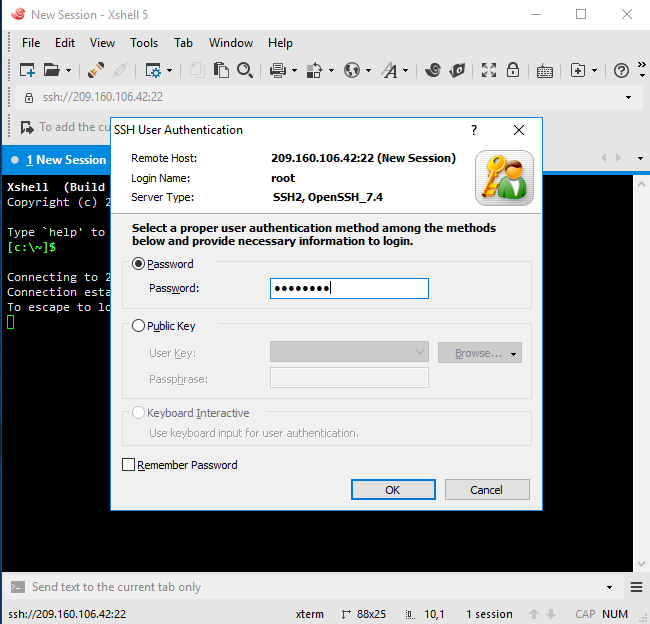
Click "OK" Xshell is connected to New Session[209.160.106.42:22). Then you can start to work now.
Partition and Format Data Volume or NVMe
For example, a new 20 GB data disk(device name: /dev/sda) creates a single-partition data disk and mounts an ext4 file system with CentOS 7.4. (Please note that Partition and Format local disk 1.4TB NVMe is same as data volume.)
1.Using the Xshell tool or VNC to connect the instance.
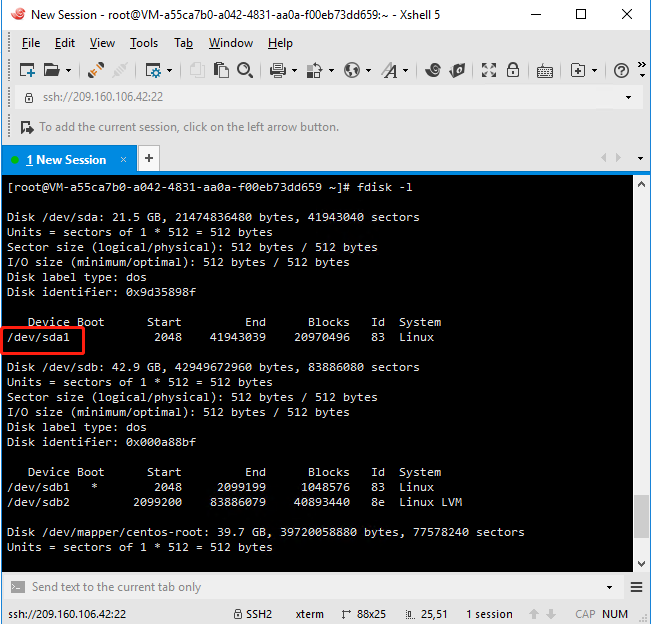
2. Run the fdisk -l command to see if the instance has a data disk. If /dev/sdb is not found after executing the command, there is no data disk for the instance and no need to format it. Then please ignore the rest of this article.
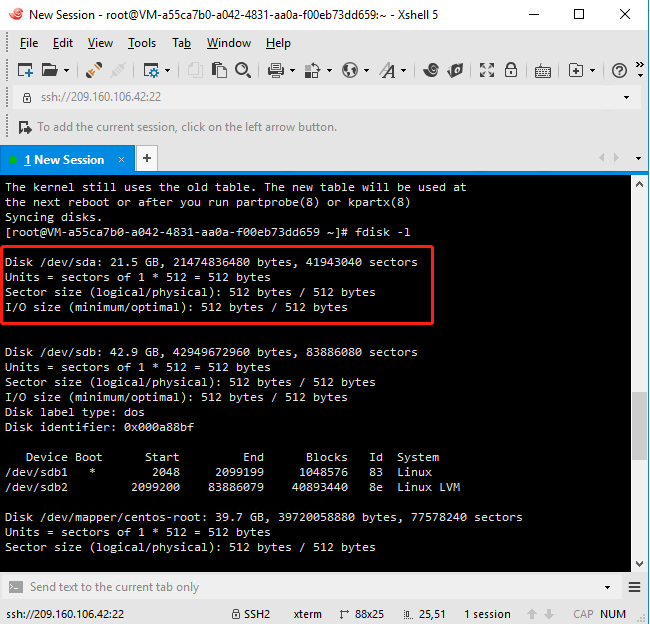
3. Create a single-partition data disk and, they execute the following commands in turn:
(1) Run fdisk /dev/sda: Partition the data disk. Please note that fdisk /dev/sda is the drive letter.
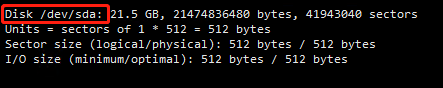
(2) Type n and press enter: Create a new partition.
(3) Enter p and press enter: Select primary partition. Because you are creating a single-partition data disk, you only need to create the primary partition.
(4) Enter the partition number and press enter. Since only one partition is created here, you can type 1.
(5) Enter the first available sector number: press enter to use the default value of 1.
(6) Enter the last sector number: Because only one partition is created here, press enter to use the default value.
(7) Enter wq and press enter to start partitioning.
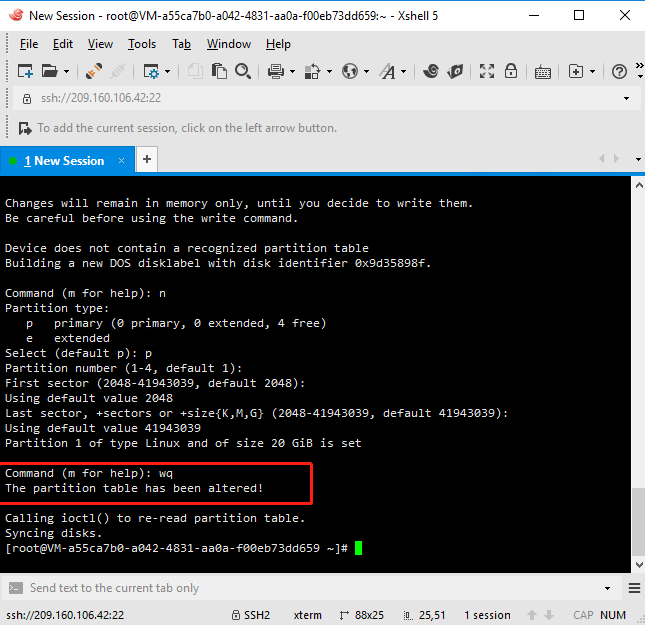
4. View new partitions: Run the command fdisk -l. If /dev/sda1 appears, the new partition, /dev/sda1, was successfully created.
5. Create a file system on the new partition: run the command mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda1 (if you need to share files between Linux and Windows systems, create a VFAT file system using mkfs.vfat).
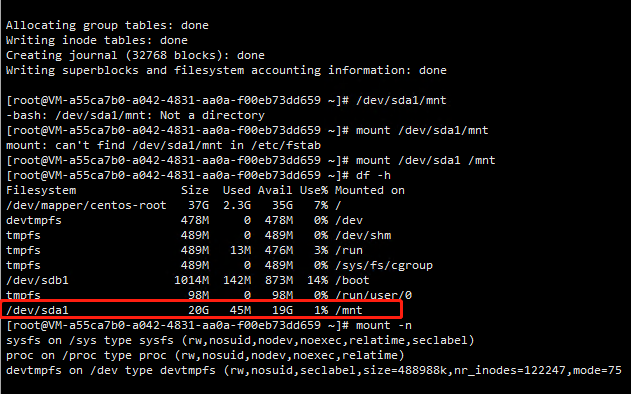
6. Mount the file system: Run the command mount /dev/sda1 /mnt (/mnt is the mount point path to mount).
7. View current disk space and usage: Run the command df-h. If a new file system message appears, the mount is successful, and the new file system is ready.
If you have any questions, please contact us at [email protected] or submit a support case.




No comments